Network Service Settings #
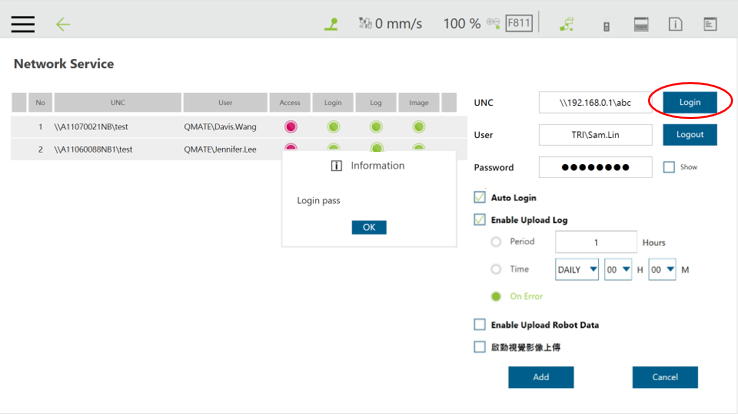
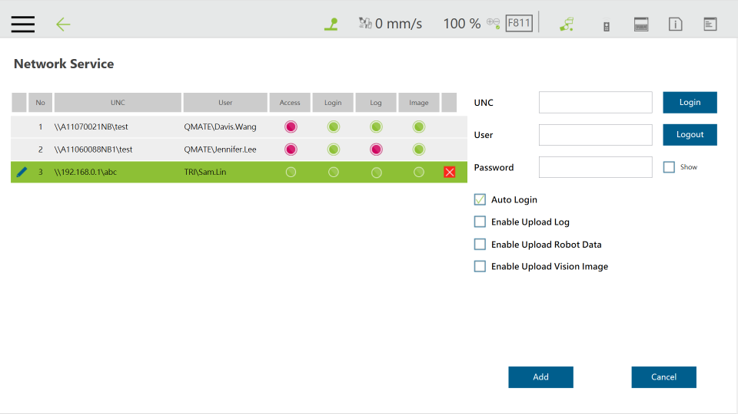
First, set up the network service
File Command #
The File command allows you to read, modify, and delete files in the shared folder. You can communicate with the robot through the RJ45 port. Before using File, make sure the port is enabled. Then, use the Command node to send corresponding strings or variables to the port, create string-type variables to accept the returned result, and based on this procedure, finish flow programming.
Log Node #
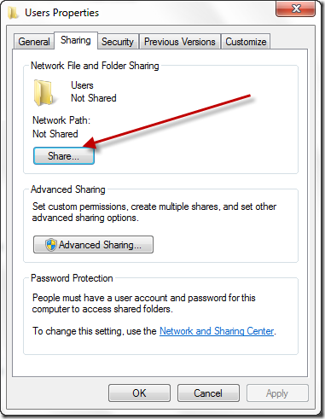
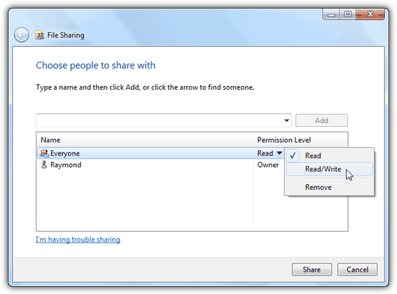
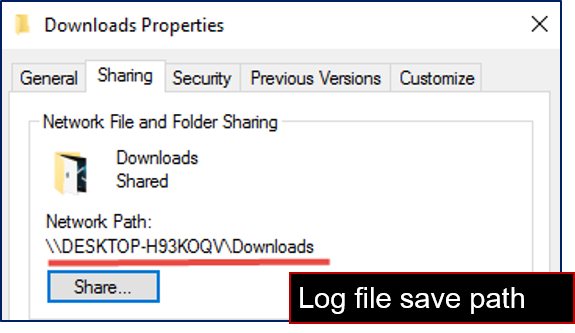
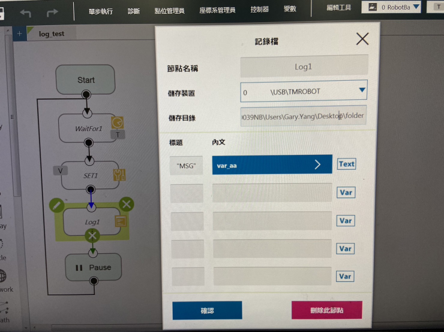
The Client can set up the network to create a shared folder and communicate with the robot through the LAN. In a TMflow project, you can use the Log node to save the variables and strings you have set up to the folder. Then you can use your own computer to view the logs saved in the Log node in the folder.
You can set a variable or string as the Content field of the Log node. The log can be saved to the FTP server of an SMB/CIFS, USB drive, or SSD.
You may also save the log locally to the Textfiles or xmlFiles directory.
Differences Between Log Node and File Command #
- You can use the File command “è” (as opposed to “exist”) to write, delete, read, or search data in a remote folder.
- The Log node accesses required txt data through a shared folder. This helps you track issues. So, you have spare time to get to know about functions related to titles and formatting.
- One important thing to note about Log is that even if the node does not work after you press the Play button, it tries to connect. In this case, wait for a while.